Are you tired of constantly changing batteries in your IoT devices? Do you have a collection of temperature sensors that are only marginally effective because of their limited range? Well, LoRa technology might be the answer to your prayers! This revolutionary technology has enabled IoT devices to take the world by storm. With their long-range and low-power communication abilities, they make life easier for those who care about the temperature, from farmers to healthcare professionals. Join me in this blog as we delve deeper into the benefits, working principle, and popular applications of LoRa temperature sensors.
What is LoRa temperature sensor
A LoRa temperature sensor is a wireless device that uses long-range, low-power radio frequency technology to monitor and transmit temperature readings over long distances. One noteworthy feature of this technology is its low power consumption, allowing for seamless data transfer of up to 10 km in rural regions and 2 km in urban areas. LoRa temperature sensors come in various forms, including standalone devices or sensors embedded in equipment or systems.
LoRa temperature sensors: how they work
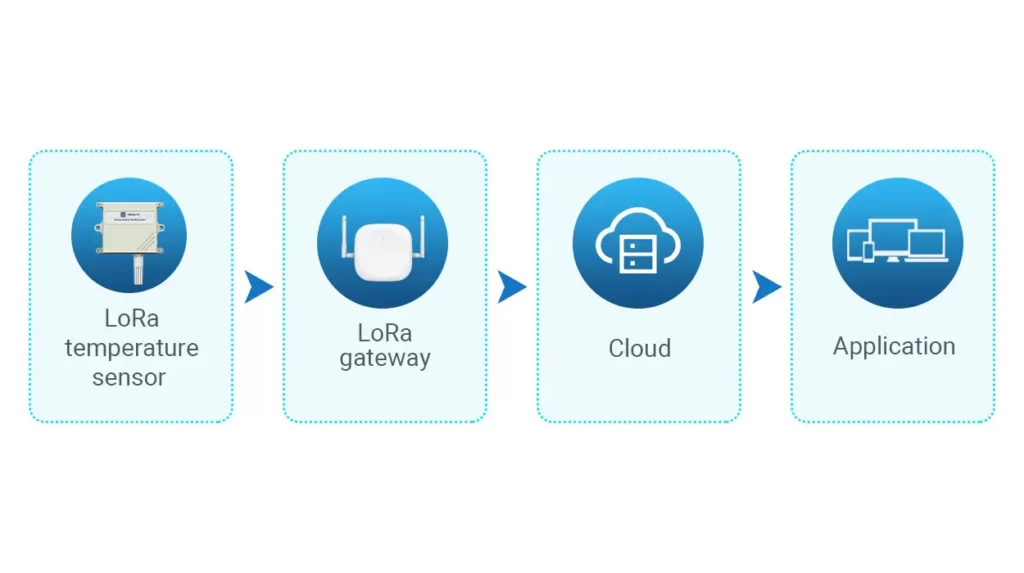
LoRa temperature sensors consist of two main components: a temperature sensor and a LoRa radio transceiver. The temperature sensor measures the temperature and sends the readings to the LoRa radio transceiver. The LoRa radio transceiver then converts the data into a LoRa signal, which is transmitted to a LoRa gateway or base station. The gateway receives the signal, converts it into data packets, and sends it to a server or cloud-based platform. The data can be accessed and analyzed in real-time using a computer, smartphone, or tablet.
Use cases of LoRa temperature humidity sensor
The LoRa temperature humidity sensor is a valuable and adaptable device with multiple applications across different industries. Its popularity stems from their cost-effectiveness, long-range transmission, and low power consumption. These attributes make them a popular choice in numerous industries. Some of the use cases of LoRa temperature humidity sensors include:

Agriculture and farming
Farmers can use LoRa temperature humidity sensors to monitor the temperature and humidity levels in crops, greenhouses, and livestock buildings. This helps farmers to optimize the growing environment and prevent loss of crops and animals due to unfavorable environmental conditions.
Industrial manufacturing
The industrial manufacturing industry can benefit from LoRa temperature humidity sensors to measure the environmental conditions in manufacturing plants and equipment rooms. These sensors can help optimize production processes, troubleshoot problems and prevent potential delays or downtime.
Food and beverage industry
In the food and beverage industry, it is necessary to keep track of the conditions in which the products are stored. LoRa temperature humidity sensors can aid in maintaining optimal conditions, which can prevent spoilage and maintain product freshness and quality.
Healthcare and pharmaceuticals
LoRa temperature humidity sensors can be used in healthcare and pharmaceuticals to monitor the temperature and humidity levels in laboratories, clinics, and hospitals. This helps to ensure that medicines and vaccines are stored in optimal conditions while ensuring their efficacy.
Supply chain and logistics
For supply chain and logistics, LoRa temperature humidity sensors can help monitor temperature-sensitive cargo conditions during transportation. Cargo loaded with perishable goods can be monitored and tracked to ensure product quality is maintained throughout transit.
Building automation and HVAC systems
The applications of LoRa temperature humidity sensors extend to building automation and HVAC systems. By incorporating smart temperature sensors, facility managers can monitor the environmental conditions and adjust for temperature and humidity variations. This helps to optimize energy consumption and maintain a comfortable indoor environment for occupants.
Benefits and limitations of LoRa temperature sensor
Since we have talked about the various applications of LoRa temperature sensors, it’s time to understand their capabilities and limitations. Knowing these factors can help maximize their benefits and reduce potential drawbacks in their application. Here are some of the benefits of LoRa temperature sensors:
- Versatile applications in various industries, including agriculture, building automation, and HVAC systems.
- Cost-effective, with low power consumption, allowing long-lasting battery life.
- Long-range transmission capabilities up to several kilometers, suitable for monitoring vast locations without requiring additional repeaters.
- Real-time monitoring data enables quick detection of changes in temperature and humidity levels, giving early warnings to optimize the environment for desired outcomes.
Despite their advantages, LoRa temperature sensors also have some limitations.
- Low power consumption sometimes comes at the cost of reduced data bandwidth, resulting in limited data transmission for high-precision applications.
- The available sensing range can be a limitation, with some models unable to measure extreme temperature and humidity levels.
- The accuracy of readings may be affected by signal interference, increasing the likelihood of false readings.
- While LoRa sensors are cost-effective, it may incur additional costs for integration with other systems, such as sensor gateways and backend servers.
LoRa temperature sensor vs other IoT temperature sensors
LoRa temperature sensors are popular due to their ability to monitor temperature in remote locations with minimal power consumption. In comparison to other IoT sensors, they excel in range, battery life, and penetration through walls. But note that they may not be suitable for all environments and can interfere with other wireless signals.
Despite the numerous advantages of LoRa, there are also some downsides to consider, including potential signal interference and integration difficulties with existing IoT networks. Other sensors such as WiFi temperature sensors are more appropriate for high-bandwidth applications, and Zigbee temperature sensors are more suited for low-power mesh networking. Bluetooth temperature sensors work best in short-range applications, and cellular network-based temperature sensors are ideal in areas where cellular data plans are available.
Therefore, when choosing the best technology option for IoT temperature monitoring, thorough research to weigh the pros and cons of each is crucial.
Best practices for using LoRa temperature sensors
LoRa temperature sensors have emerged as an ideal solution for long-range and reliable temperature monitoring in various industrial and commercial applications. With the right selection and implementation practices, LoRa temperature sensors can provide accurate and valuable data to businesses, enabling them to make informed decisions and monitor their environment more effectively.
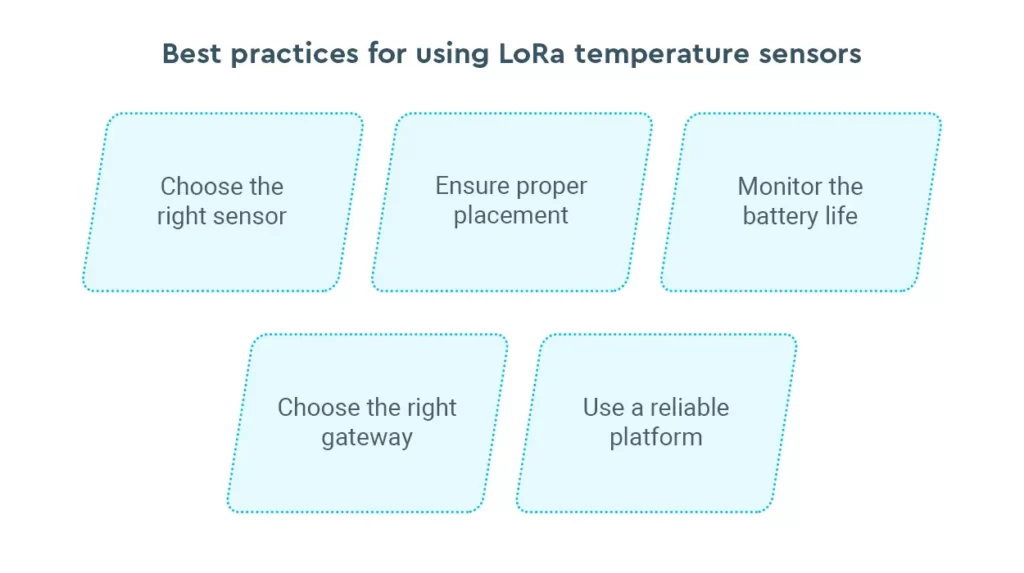
Choose the right sensor: Make sure to select the right type of LoRa sensor based on your specific needs. Since LoRa sensors come in different types, consider factors such as temperature range, accuracy, and measurement frequency when making your selection.
Ensure proper placement: The location of the temperature sensor is critical for accurate readings. Place the sensor close to the heat source or in the middle of the space you are monitoring for temperature to yield the most accurate data.
Monitor the battery life: LoRa temperature sensors may be battery-operated, so it’s important to keep an eye on the battery life to ensure continuous operation. However, some LoRa sensors might come with options for easy battery replacement.
Choose the right gateway: Choose a gateway that offers satisfactory coverage for your needs. A gateway with higher output power can be helpful for long-range applications. The proper LoRa gateway is essential for the performance of your temperature monitoring system. Consider connectivity, compatibility, and other factors when choosing a gateway.
Use a reliable platform: Use a reliable platform for data management and analysis. A cloud-based platform can offer real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities, making it easier for businesses to identify temperature changes and act promptly if there is a deviation from preset limits.
What is the cost of LoRa temperature sensor
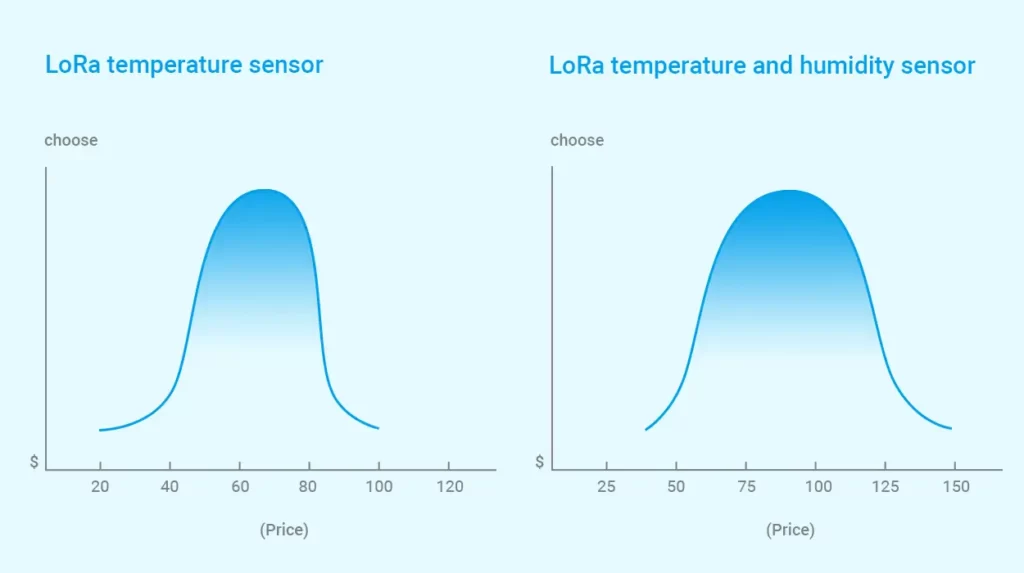
LoRa temperature sensors are an affordable and reliable option for monitoring temperature levels across different settings. The cost of these sensors can vary based on brand, model, and features, with standalone LoRa temperature sensors that can range from around $20 to $100 or more. However, LoRa temperature and humidity sensors may cost around $30 – $150 due to the additional measurement capability.
It is crucial to consider the cost of a LoRa gateway as an additional expense when implementing a LoRa temperature sensor system. LoRa gateways typically cost between $50 to $300, depending on the model and specific features needed.
Despite the slightly higher initial investment compared to traditional sensors, LoRa temperature sensors and LoRa humidity sensors provide significant savings in the long run through their highly efficient, energy-saving, and long-range communication capabilities. They can also be seamlessly integrated into IoT systems, making it easier to monitor and regulate temperature and humidity levels efficiently.
Conclusion
Overall, LoRa LoRaWAN temperature sensors offer the best of both worlds: they are wireless, highly secure, and offer long-range connectivity. They are perfect for monitoring temperature in difficult-to-reach environments and areas where conditions frequently change. As more industries adopt the use of LoRa temperature sensors, it is evident that we are witnessing the future of temperature monitoring. It is time to invest in this innovative technology to ensure that your equipment and products stay at suitable temperatures at all times.